English
kötelező
gyakorlati jegy
5
1
4
60
30
Department of Food Hygiene (DFH)
- Vet EN
Course description
1. Characteristics of the curriculum
Feature: obligatory subject
Department: Department of Food Hygiene
Timing in the curriculum: Semester 9-10
Lectures/practical: 120/60
- Semester 9: 60/30
- Semester 10: 60/30
Credit:
- Semester 9: 4
- Semester 10: 6
2. Topics
Lectures
In the framework of lectures the theoretical basis of the complex knowledge of hygiene conditions and legal requirements of production, processing and trade of wholesome foodstuffs are presented to develop the thinking and skill of Veterinary Public Health.
In Semester 9, the following topics will be discussed: general fundamentals of food hygiene include the basic terms, foodborne hazards and the potential adverse health, main aspects of food microbiology and chemical-toxicological food safety, risk assessment and risk management of microbiological and chemical risks, risk communication, basic knowledge on food spoilage and preservation, background of food-chain safety legal regulation, the general rules of food production, processing and marketing, food adulteration.
In Semester 10 the food chain safety tasks with a one health approach will be presented, focusing on production chains. Initially, the ruminant production chain will be discussed including milk hygiene (production and processing) built on the previous fundamentals, then during the topics of meat hygiene the different production chains – cattle and other ruminants, swine, poultry, fish, and other animals production chain – will be summarised, furthermore the processing hygiene and safety aspects of foodstuffs of plant origin, alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages and meat substitutes will be summarised. Special attention will be paid to meat inspection, animal welfare of food-producing animals, to present the food processing technology of foods of animal and plant origin, and to make known the processing hygiene aspects of them.
Practicals
The purpose of food hygiene practicals is to demonstrate the practical aspects of the theoretical knowledge discussed in the lectures as well as to carry out the manual exercise of certain technological processes, and to develop the practical skills necessary to develop a complex way of thinking about the safety of the food chain.
3. How to be prepared for and how execute the practicals
The base of group division is the list given by the secretariat of International Study Program. The total number of one group cannot exceed 20 students.
The student should be arrived in time, in clean white-coat and well-prepared to the site of practicals.
Due to the actual pandemic situation of infectious diseases, all students must keep the actual regulations/rules (e. g. disinfection of hands direct prior to start of practicals, wearing masks covering both nose and mouth during the whole practical time etc.).
In case of symptoms suggestive of fever or suspected Covid or other infectious disease, the student should not participate in the exercises.
4. The way of check of knowledge during the practicals
It may be performed in oral or written forms. It is primarily directed to the check of knowledge related to the given week-topic, but the topics of the previous weeks are also interrogated continuously.
5. How to supplement the practicals
If somebody is not able to participate on the practical in the right time, the supplementation is possible during the semester at a time point agreed upon with the instructor of the given practical in advance in written form (via e-mail). Supplementation of missing because of the obligatory clinical practice (2 weeks) is not needed. It is certified directly towards the Department by the given clinical department. The number of the missed practicals can be max. four (4) practicals (including the 2 weeks obligatory clinical practice), above this the signature by the end of the semester will be denied.
The participation in practicals and the rules of retake are subjected to change based on the actual infectious pandemic situation.
6. Midterm tests, their evaluation, and their supplementation if necessary
During Semester 9, students will have two written midterm tests. The materials of these tests are based on the previous topics of practicals and lectures up to the time of tests. The tests are evaluated with percentage values based of the total scores with a minimum passing score of 60%.
If any of the midterm tests is failed or the student was not able to participate, he/she must write a supplementary midterm test at least up to the end of the semester. Altogether, there are two additional chances for retake.
The student who prepares a written case study about the theoretical topics given on the lecture, and it is submitted to the Department till the last week of education period, and it is accepted by the lecturer performed the topic, is exempted from the writing of the first midterm test in the Semester 10, fulfils it with 100% result.
During Semester 10, there will be two written midterm tests, as well based on the topics of the lectures and the practicals up to the time of tests. A minimum of 60% should be reached to pass the tests. If any of the midterm tests is failed or the student was not able to participate, he/she must write a supplementary midterm test at least up to the end of the semester. Altogether, there are two additional chances for retake. If someone fails to meet the minimum requirement of 60% in case of any of the midterm tests, the signature at the end of the semester will be denied.
7. Signature by the end of the Semester, conditions of having a practical mark
Semester 9 and 10: Participation on the lectures is obligatory (according to the University’s SOP). Occasionally, the participation is checked by the lecturers. In the case of more than 3 missing lectures that are not certified, the signature of the semester will be refused.
Requirements for signature by the end of both semesters (Semester 9 and 10) are the participation in all the practicals and appropriate results of the two written midterm tests.
Semester 9: Practical mark: The practical course grade is calculated as an average of the midterm tests as follows: 60-69% = 2, passing; 70-79% = 3, fair; 80-89% = 4, good; 90-100% = 5, excellent.
If someone fails to meet the minimum requirement of 60% in case of any of the midterm tests, the practical course grade at the end of Semester 9 will be 1, i.e., failed.
If the mark is wished to be improved, it may be done in the exam period.
The conditions of having the credit points according to the curriculum are the signature by the end of the Semester and at least a practical course grade 2.
Semester 10: the condition of having the signature is the participation in the lectures and the practicals, and the minimum 60% fulfilment of both midterm tests.
The participation in practicals and the rules of retake are subjected to change based on the actual infectious pandemic situation.
8. Exam requirements
Semester 9: no exam (practical course grade)
Semester 10: final exam based on the materials of Semesters 9 and 10
9. Semester 10 final exam
The final exam consists of two parts. The first one is a written exam that includes the materials of the lectures and practices of both semesters 9 and 10, whereas the second, oral exam is focused on the most important topics of the one-day competence. Both part-exams will be assessed with marks between 1 and 5 the average of which gives the final mark of the exam. The written part of the exam will be evaluated as follows: 60-69% = 2, passing, 70-79% = 3, fair, 80-89% = 4, good, 90-100% = 5, excellent. Both the written and the oral parts of the exam must be passed. If the written part is failed, the student cannot follow the exam with the oral part, i. e. the precondition of the oral exam is to pass the written part. If someone fails at the written part, cannot attend at the oral one. However, if the oral part is unsatisfactory, only this part should be retaken. If the result of the written and/or oral exam is unsatisfactory, the next exam is considered as a retake exam.
The oral part of the exam is evaluated as unsatisfactory (1=failed) if there are significant gaps in the knowledge of the student on the topic in relation to the one-day competence. At the oral exam students draw two questions from the previously published list of altogether 40 complex questions.
10. Suggested learning materials
Materials of lectures and practicals (e-learning system).
Laczay, P: Food hygiene, food chain safety. Textbook, Budapest, 2014.
Erdősi, O.-Lányi, K.-Lehel, J.-Szili, Zs.: Food hygiene practicals I. A/3 Nyomdaipari és Kiadói Szolgáltató Kft., Budapest, 2016.
Erdősi, O.-Lányi, K.-Lehel, J.-Szili, Zs.: Food hygiene practicals II. A/3 Nyomdaipari és Kiadói Szolgáltató Kft., Budapest, 2017.
11. Timetable
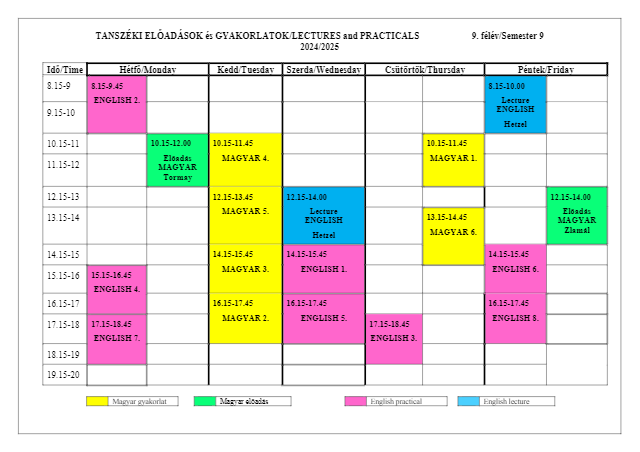
Lectures theme
LECTURES ON FOOD HYGIENE
Academic year 2024/2025, Semester 9
Wednesday 12:15-14:00 / Hetzel lecture room
Friday 8:15-10:00 / Hetzel lecture room
| Week | Date | Topics | Name of Lecturer |
| 1 | 11/09
|
Introduction and history of food hygiene. One-health.
Food safety-food security. |
Miklós Süth
|
| 13/09 | The food arena. The “good” food. | László Búza | |
| 2 | 18/09 | Introduction to food chain risks. Basics of risk assessment. risk-benefit analysis. | Ákos Jóźwiak |
| 20/09 | Basic principles of food law. Legal regulation of the food economy. | Gyula Kasza | |
| 3 | 25/09 | Food chain control system, traceability, responsibility in the food chain. | Tibor Kocsner |
| 27/09 | Basics of the food microbiology. Growth and destruction of microbes. | Attila Nagy | |
| 4 | 02/10 | Obligate pathogenic bacteria in food. | Lancz Zsuzsanna |
| 04/10 | Facultative pathogenic bacteria, bacterial toxins, viruses, prions, parasites. | Slaven Grbic | |
| 5 | 09/10 | Microbial spoilage. Application of microorganisms in food industry. | Tekla Engelhardt |
| 11/10 | Reduction of microbiological risks. | Tekla Engelhardt | |
| 6 | 16/10 | Disinfection. | Zsuzsanna Lancz |
| 18/10 | Chemical-toxicological food safety: veterinary medicinal products (VMP) and prohibited active substances. | József Lehel | |
| 7 | 25/10 | Chemical-toxicological food safety: technological pollutants.
Contaminants of biological origin I. (mycotoxins, fungal toxins) |
Dániel Pleva |
| 25/10
18:15 |
Chemical-toxicological food safety: agricultural and environmental originated contaminants of food. HETZEL lecture room | Katalin Lányi | |
| 8 | 30/10 | Contaminants of biological origin II. (marine and freshwater biotoxins). Toxic substances of natural origin. | József Lehel |
|
9 |
06/11 | Antibiotic resistance in food chain
Control of chemical contaminations. Reduction of chemical risks. |
Ákos Jóźwiak
Zsuzsa Farkas |
| 08/11 | Food Contact Materials (FCM).
Food packaging and labelling. |
Lívia Darnay | |
|
10 |
13/11 | Food safety and quality relationships of primary and secondary food production and transport. | László Búza |
| 15/11 | Prerequisite programs. GAP, GMP, GHP. | Slaven Grbic | |
|
11 |
20/11 | Basic knowledge of HACCP system. | Slaven Grbic |
| 22/11 | Implementation of the HACCP system. | Slaven Grbic | |
|
12 |
27/11 | Risk management. Risk benefit analysis. | Ákos Jóźwiak |
| 29/11 | Investigation of food chain safety incidents.
Diagnosis and management of food-borne/mediated diseases. |
László Búza | |
|
13 |
04/12 | Food adulteration. | László Búza
Lívia Darnay |
| 06/12 | Food allergy and food intolerance. | Béla Gyetvai | |
| 14 | 11/12 | Risk communication. | Gyula Kasza |
| 13/12 | Sustainability in the food chain. Food waste – problems and solutions. | Gyula Kasza |
Practical lessons theme
Food hygiene practicals
Academic year 2024/2025, Semester 9
Place of practical: “N” building 2nd floor
| Week | Date | Topics | Supervisor | Instructor |
| 1 | 09-13. 09. | Aims and requirements of practicals, occupational health rules. | József Lehel
Katalin Lányi |
Lívia Darnay
Dániel Pleva Máté Farkas |
| 2 | 16-20. 09. | Food sampling – official sampling and sampling by the food business operators.
|
József Lehel | Lívia Darnay
Dániel Pleva Máté Farkas |
| 3 | 23-27. 09. | Monitoring systems. | József Lehel | Lívia Darnay
Dániel Pleva Máté Farkas |
| 4 | 30.09- 04.10 | Food hygiene significance and examination of water. | Katalin Lányi
Attila Nagy |
Lívia Darnay
Dániel Pleva Máté Farkas |
| 5 | 07-11. 10. | Food microbiological criteria – application of 2073/2005 EC regulation –Personal hygiene examination. | Attila Nagy
Tekla Engelhardt |
Lívia Darnay
Dániel Pleva Máté Farkas |
| 6 | 14-18. 10. | Classic and rapid microbiological examinations in the food microbiology. | Attila Nagy
Tekla Engelhardt |
Lívia Darnay
Dániel Pleva Máté Farkas |
| 7 | 21-25. 10. | Detection of pathogens from food (Salmonella detection)
|
Attila Nagy
Tekla Engelhardt |
Lívia Darnay
Dániel Pleva Máté Farkas |
| 8 | 28.10-01.11. | Molecular methods in food microbiology.
Evaluation of the PCR results (Salmonella) |
Attila Nagy
Tekla Engelhardt |
Lívia Darnay
Dániel Pleva Máté Farkas |
| 9 | 04-08. 11 | Laboratory methods for monitoring of food businesses
Trichinella testing. |
András Bittsánszky
Tekla Engelhardt László Búza |
Lívia Darnay
Dániel Pleva Máté Farkas |
| 10 | 11-15. 11. | Chemical-toxicological food safety: sample preparation, screening investigations, confirmatory, large instrument analysis. | Katalin Lányi
József Lehel |
Lívia Darnay
Dániel Pleva Máté Farkas |
| 11 | 18-22. 11. | Chemical and microbiological risk assessments: case studies. | Ákos Jóźwiak | Lívia Darnay
Dániel Pleva Máté Farkas |
| 12 | 25.-29. 11. | HACCP system: case studies.
|
Ákos Jóźwiak
András József Tóth |
Lívia Darnay
Dániel Pleva Máté Farkas |
| 13 | 02- 06. 12. | Risk management: case studies. | Ákos Jóźwiak | Lívia Darnay
Dániel Pleva Máté Farkas |
| 14 | 09-13. 12. | Supplementary practical. | Lívia Darnay
Dániel Pleva Máté Farkas |
Evaluation description
